
Elimination Reactions
E1cB Mechanism
The base abstracts a proton from the alkyl halide resulting in a carbanion which is the conjugate base of the alkyl halide and in the next step the negative charge forms a π-bond pushing out the leaving group.
This is termed as E1cB (E1 conjugate base).
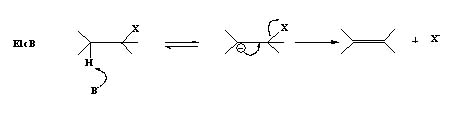
- Less common because the anion formed is so unstable that it breaks down as the proton is being removed.
- A two step process.
- E1cB is favored if the anion is stabilized and has a poor leaving group and a strong base is used.
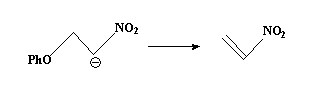
Nitro group stabilizes the carbanion and the PhO group is a poor leaving group.
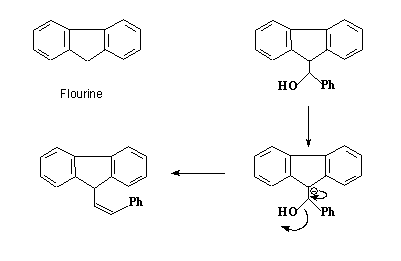
- –OH is a bad leaving group.
- Anion formed is stabilized ( aromatic 14 electron system)
- Rare example of a –OH as leaving group(without protonation)
Copyrights: 2005 www.chemvista.org All Rights Reserved